随着时代的发展,单一研究转录组、蛋白代谢、甲基化等已经难以满足研究者越来越高的研究期望,大家更多地期望联合多种数据进行多组学联合分析。那么这时候,一种好的展示结果的方式无疑会为发表高分文章增光添彩。
诚然,小编的上一篇(如何让你的图变得高大上之ComplexHeatmap())结局得太匆匆,因此,本篇奉上作图代码实例。
本次,我们将展示一个甲基化与表达谱联合分析的热图。本着先学习再创造的态度,小编做了一下知识的搬运工,本篇所有代码均引用自:Zuguang Gu, Roland Eils and Matthias Schlesner, Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data, Bioinformatics, 2016。
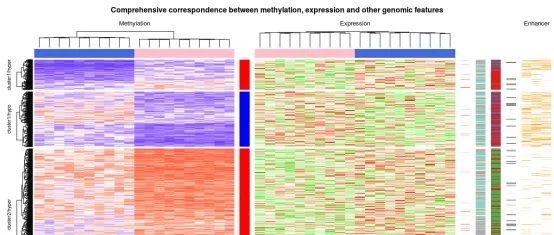
我们先上效果图: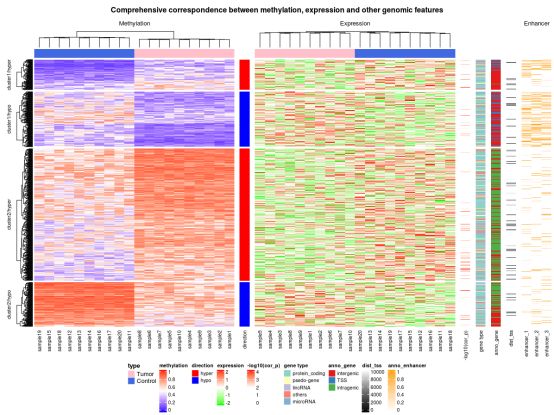
其实代码并不长,关键在于如何准备作图所用数据以及对代码的理解上,所以下面将着重对这两点进行解释说明。
>library(ComplexHeatmap)
>library(circlize)
#为了测试方便,用setwd设置工作路径
setwd(“/media/bmk/***/Meth_Exp”)
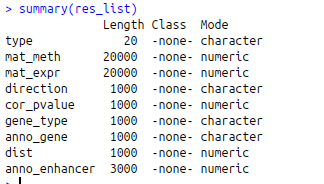
#rds格式是一种保存了数据的数据类型和结构的格式,可以用函数saveRDS()来生成这种格式的文件。meth.rds文件来自R包示例文件,如需查看这个文件中都是什么,请参考(看不清热图的聚类结果怎么办)的方法。另外,文件中只包含了DMR关联基因的甲基化和表达量呈现负相关的DMR
>res_list = readRDS(“data/meth.rds”)
#显示样本是肿瘤样本还是正常样本的标签
>type = res_list$type
(20个正常样本和20个肿瘤样本)
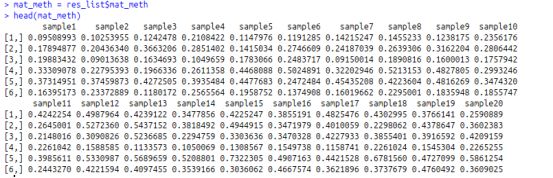
#矩阵,其中行对应差异甲基化区域(DMR),矩阵中的值是每个样品中DMR中的平均甲基化水平。
>mat_meth = res_list$mat_meth
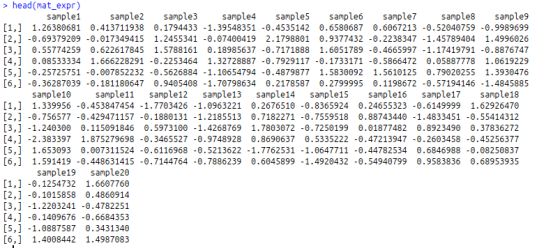
#矩阵,其中行对应于与DMR相关的基因(即与DMR最近的基因,也可以叫做DMR关联基因),矩阵中的值是每个样品中每个基因的表达水平(对样品中的每个基因的表达进行了标准化)。
>mat_expr = res_list$mat_expr
#甲基化变化的方向(hyper表示肿瘤样本中高甲基化,hypo表示肿瘤样本中低甲基化)
>direction = res_list$direction
#甲基化与甲基化关联基因相关性p值
>cor_pvalue = res_list$cor_pvalue
#基因类型(如蛋白编码基因或lincRNA等)
>gene_type = res_list$gene_type
#DMR注释到基因的功能区间(如intergenic/intragenic或者TSS
>anno_gene = res_list$anno_gene
#DMR到关联基因TSS的距离
>dist = res_list$dist
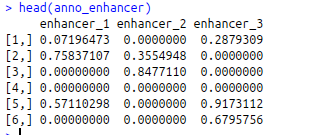
#与增强子重叠的DMR的部分
>anno_enhancer = res_list$anno_enhancer
#颜色定义参见上一篇(如何让你的图变得高大上之ComplexHeatmap()) ##我们首先定义两个列注释,然后制作复杂的热图。 >ht_global_opt( #Heatmap()实际上是单一热图的类构造函数。如果需要组合超过一个热图,用户可以通过+操作符添加热图。默认情况下,将两个热图通过+连接后,第二个热图的行聚类树会去掉,行的顺序会与是第一个热图的顺序保持一致。
##首先计算甲基化矩阵的列聚类,以便可以将表达矩阵中的列调整为具有与甲基化矩阵中相同的列顺序。
>column_tree = hclust(dist(t(mat_meth)))
>column_order = column_tree$order
>library(RColorBrewer)
#定义甲基化表达水平颜色,从0/blue-0.5/white-1/red渐变
>meth_col_fun = colorRamp2(c(0, 0.5, 1), c(“blue”, “white”, “red”))
#定义甲基化变化方向对应颜色
>direction_col = c(“hyper” = “red”, “hypo” = “blue”)
#定义表达水平颜色
>expr_col_fun = colorRamp2(c(-2, 0, 2), c(“green”, “white”, “red”))
#定义相关性p值颜色
>pvalue_col_fun = colorRamp2(c(0, 2, 4), c(“white”, “white”, “red”))
#定义基因类型颜色
>gene_type_col = structure(brewer.pal(length(unique(gene_type)), “Set3”),
names = unique(gene_type))
#定义注释model颜色
>anno_gene_col = structure(brewer.pal(length(unique(anno_gene)), “Set1”),
names = unique(anno_gene))
#定义距离颜色
>dist_col_fun = colorRamp2(c(0, 10000), c(“black”, “white”))
#定义增强子相关颜色
>enhancer_col_fun = colorRamp2(c(0, 1), c(“white”, “orange”))
#ht_global_opt()是一个可选函数,它会全局控制一些参数。我们可以通过此全局函数同时为所有热图/注释设置一些参数。需要注意的是,一定将它放在热图代码(也就是Heatmap())之前,并在绘制热图后重置所有选项值以消除对下一个热图的影响。
#可以通过?ComplexHeatmap::ht_global_opt查看此函数的帮助
> names(ht_global_opt()) #可查看该函数可定义的参数
[1] “heatmap_row_names_gp”
[2] “heatmap_column_names_gp”
[3] “heatmap_row_title_gp”
[4] “heatmap_column_title_gp”
[5] “heatmap_legend_title_gp”
[6] “heatmap_legend_title_position”
[7] “heatmap_legend_labels_gp”
[8] “heatmap_legend_grid_height”
[9] “heatmap_legend_grid_width”
[10] “heatmap_legend_grid_border”
[11] “annotation_legend_title_gp”
[12] “annotation_legend_title_position”
[13] “annotation_legend_labels_gp”
[14] “annotation_legend_grid_height”
[15] “annotation_legend_grid_width” [16] “annotation_legend_grid_border”
[17] “fast_hclust”
heatmap_legend_title_gp = gpar(fontsize = 8, fontface = “bold”),
heatmap_legend_labels_gp = gpar(fontsize = 8),
heatmap_column_names_gp = gpar(fontsize = 8),
heatmap_column_title_gp = gpar(fontsize = 10),
heatmap_row_title_gp = gpar(fontsize = 8)
)
#利用HeatmapAnnotation()对行或列注释。HeatmapAnnotation()函数会生成一个注释用的list对象。该函数的主要格式是HeatmapAnnotation(df/数据框, name/注释名称, col/注释颜色列表, show_legend/是否显示数据框中每一列的图例)
#样本类型注释,Tumor样本为pink,Control样本为royalbule,名称在左边
>ha = HeatmapAnnotation(type = type,
col = list(type = c(“Tumor” = “pink”, “Control” = “royalblue”)),
annotation_name_side = “left”)
#不显示图例名称
>ha2 = HeatmapAnnotation(type = type,
col = list(type = c(“Tumor” = “pink”, “Control” = “royalblue”)),
show_legend = FALSE)
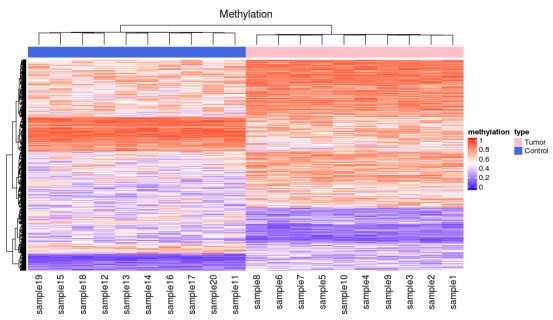
>ht_list = Heatmap(mat_meth, name = “methylation”, col = meth_col_fun,
column_order= column_order,
top_annotation = ha, column_title = “Methylation”) +
#方向部分
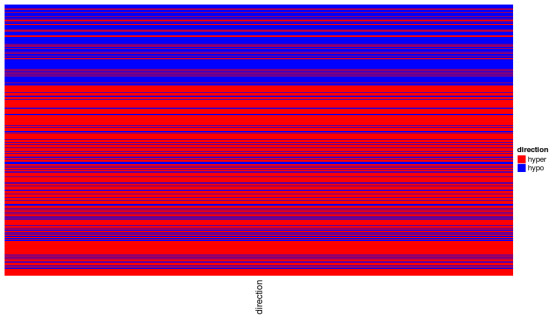
Heatmap(direction, name = “direction”, col = direction_col) +
#表达部分
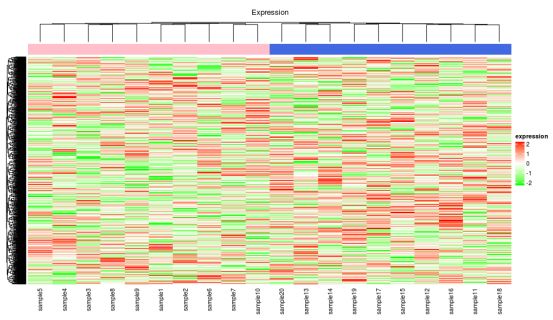
Heatmap(mat_expr[, column_tree$order], name = “expression”,
col = expr_col_fun,
column_order = column_order,
top_annotation = ha2, column_title = “Expression”) +
#p值部分
Heatmap(cor_pvalue, name = “-log10(cor_p)”, col = pvalue_col_fun)+

#基因类型部分
Heatmap(gene_type, name = “gene type”, col = gene_type_col) +
#基因注释部分
Heatmap(anno_gene, name = “anno_gene”, col = anno_gene_col) +
#距离部分
Heatmap(dist, name = “dist_tss”, col = dist_col_fun) +

#增强子部分
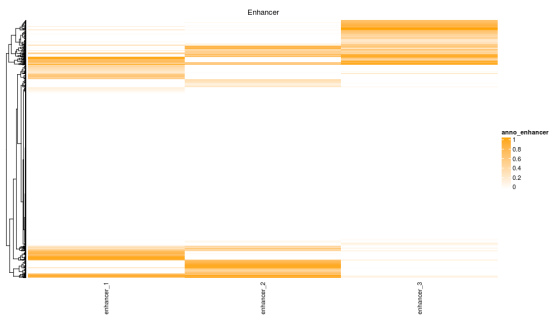
Heatmap(anno_enhancer, name = “anno_enhancer”, col = enhancer_col_fun,
cluster_columns = FALSE, column_title = “Enhancer”)
#以上热图相加后得到的是
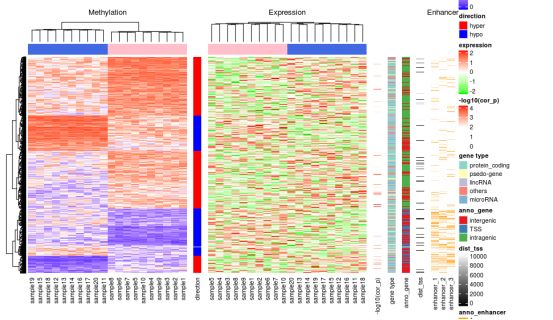
#可以看到,整个热图是单个热图从左到右依次相加,图例是从上到下依次相加,除了第一个热图的行聚类树保留了之外,其他的都默认被去除掉,顺序和第一个热图保持一致。
#热图相加的返回值是一个HeatmapList对象。直接允许ht_list对象会默认调用draw()方法。通过显式地调用draw()方法,你可以进行更多的控制,例如图例和标题。
#可以通过??`draw,HeatmapList-method`来查看draw的帮助
#分两个cluster进行聚类,按hyper和hypo进行分裂,加上整张热图的名称,设置图例位置等
>draw(ht_list, km = 2, split = direction,
column_title = “Comprehensive correspondence between methylation,
expression and other genomic features”,
column_title_gp = gpar(fontsize = 12, fontface = “bold”),
merge_legends = TRUE, heatmap_legend_side = “bottom”)
#重置全局参数消除影响
>ht_global_opt(RESET = TRUE)
复杂的热图显示高度甲基化的DMR富含基因间和基因内区域,很少与增强子重叠。相反,低甲基化的DMR富含转录起始位点(TSS)和增强子。
知识点总结
1.ComplexHeatmap可实现单个热图的相加以实现数据之间的联合。
2.ht_global_opt()函数可实现整个热图的全局控制,但要注意使用结束后进行重置。
3.draw()函数在返回值是HeatmapList对象可以实现更多的控制。








 京公网安备 11011302003368号
京公网安备 11011302003368号