Illumina Sequencing Platform

HiSeq 2500

NovaSeq 6000

Miseq
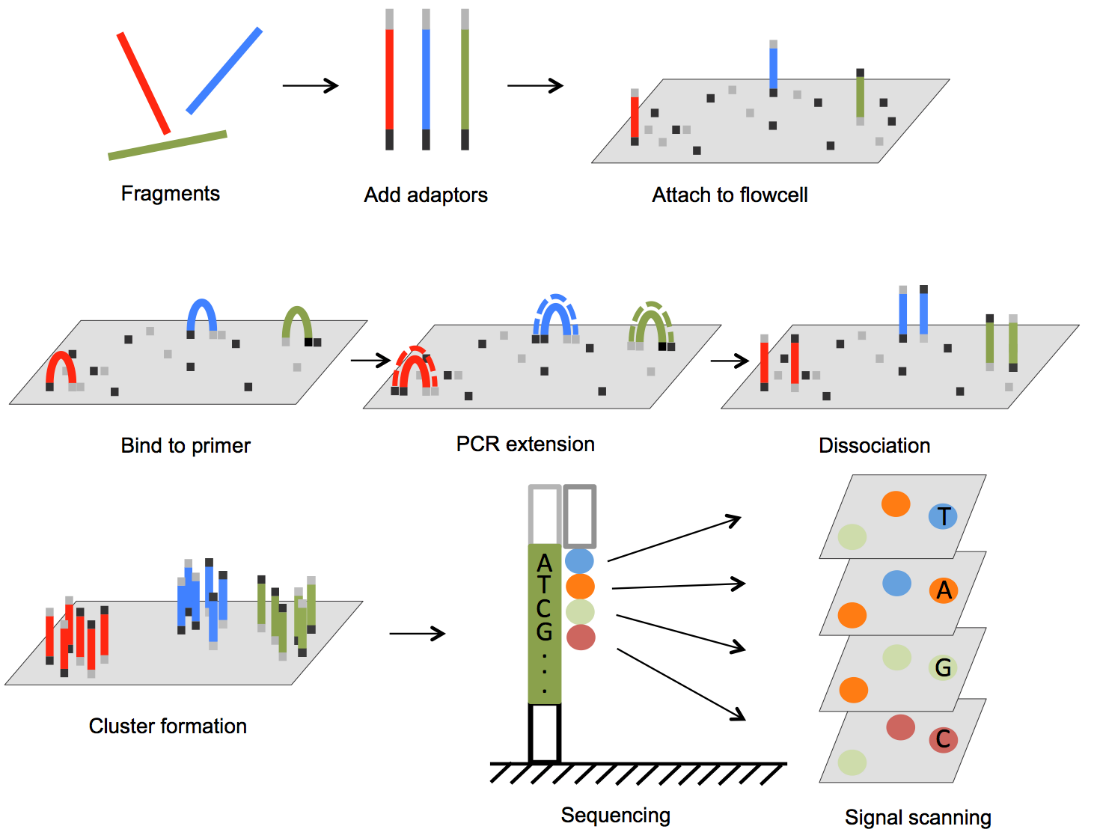
Sequencing Principle
Illumina sequencing technology, sequencing by synthesis (SBS), is a widely adopted next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology worldwide, responsible for generating more than 90% of the world’s sequencing data. A fluorescently labeled reversible terminator is imaged as each dNTP is added, and then cleaved to allow incorporation of the next base. Since all 4 reversible terminator-bound dNTPs are present during each sequencing cycle, natural competition minimizes incorporation bias. The method virtually eliminates errors and missed calls associated with strings of repeated nucleotides (homopolymers). Illumina sequencing by synthesis technology supports both single-read and paired-end libraries. SBS technology offers a short-insert paired-end capability for high-resolution genome sequencing, as well as long-insert paired-end reads for efficient sequence assembly, de novo sequencing, and more. The combination of short inserts and longer reads increases the ability to fully characterize any genome.
Application
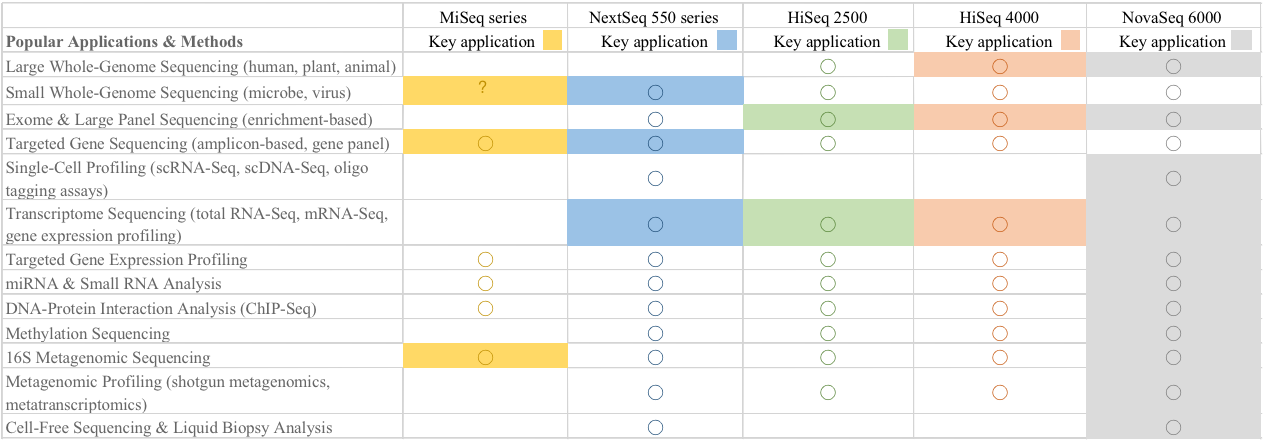

The massively parallel sequencing technology known as next-generation sequencing (NGS) has revolutionized the biological sciences. With its ultra-high throughput, scalability, and speed, NGS enables researchers to perform a wide variety of applications and study biological systems at a level never before possible. For example, NGS allows researchers to:
- Rapidly sequence whole genomes
- Zoom in to deeply sequence target regions
- Utilize RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) to discover novel RNA variants and splice sites, or quantify mRNAs for gene expression analysis
- Analyze epigenetic factors such as genome-wide DNA methylation and DNA-protein interactions
- Sequence cancer samples to study rare somatic variants, tumor subclones, and more Study microbial diversity in humans or in the environment
Today’s complex genomic research questions demand a depth of information beyond the capacity of traditional DNA sequencing technologies. Next-generation sequencing has filled that gap and become an everyday research tool to address these questions.
Actual Data Cases (DNA)
| Sample | Total base | GC% | Q20 | Q30 |
| Animal A | 290,656,560,000 | 45.76% | 97.36% | 93.17% |
| Animal B | 213,606,203,550 | 49.24% | 97.69% | 93.39% |
| Animal C | 210,366,861,900 | 43.89% | 97.69% | 93.64% |
| Crop A | 652,069,548,900 | 44.48% | 97.50% | 93.12% |
| Crop B | 630,437,499,450 | 43.07% | 97.49% | 93.12% |
| Crop C | 196,464,366,000 | 41.84% | 97.93% | 93.82% |
| Fish A | 709,093,618,800 | 40.20% | 98.14% | 94.43% |
| Fish B | 223,142,017,050 | 39.81% | 97.55% | 93.62% |
| Fruit A | 552,240,696,450 | 39.61% | 97.49% | 93.03% |
| Fruit B | 118,957,943,400 | 41.67% | 97.63% | 93.26% |
| Fruit C | 36,154,122,000 | 40.77% | 97.60% | 93.32% |
| Plant A | 496,834,286,250 | 38.63% | 97.15% | 92.23% |
| Plant B | 348,891,774,000 | 47.72% | 97.58% | 93.42% |
| Plant C | 296,097,384,900 | 50.89% | 98.03% | 94.27% |
| Fungi | 42,317,053,800 | 47.58% | 97.77% | 93.72% |
Actual Data Cases (RNA)
|
Sample |
Total base |
rRNA% |
GC% |
Q20 |
Q30 |
| Animal A | 81,849,863,700 | 0.22% | 47.48% | 97.73% | 93.72% |
| Animal B | 76,301,837,700 | 3.03% | 50.22% | 97.88% | 94.45% |
| Animal C | 69,114,559,500 | 0.52% | 51.56% | 97.83% | 94.39% |
| Crop A | 938,162,639,100 | 4.78% | 43.76% | 98.01% | 94.45% |
| Crop B | 644,816,784,000 | 7.48% | 54.33% | 97.92% | 94.33% |
| Crop C | 388,181,186,700 | 1.65% | 54.22% | 98.06% | 94.69% |
| Plant A | 501,748,230,600 | 2.16% | 45.83% | 97.97% | 94.24% |
| Plant B | 296,039,240,400 | 17.27% | 55.76% | 97.59% | 93.71% |
| Plant C | 257,524,974,750 | 0.69% | 43.78% | 97.68% | 93.46% |
| Fruit A | 272,597,781,750 | 2.95% | 47.69% | 97.86% | 93.97% |
| Fruit B | 235,173,258,000 | 3.23% | 45.00% | 97.76% | 93.57% |
| Fruit C | 165,804,670,350 | 0.68% | 47.10% | 98.02% | 94.35% |
| Fungi A | 172,958,883,900 | 0.83% | 58.36% | 97.78% | 94.13% |
| Fungi B | 158,732,967,900 | 2.79% | 53.98% | 98.22% | 95.07% |
| Fungi C | 3,558,873,450 | 0.42% | 57.95% | 97.92% | 94.71% |
Successful cases





 京公网安备 11011302003368号
京公网安备 11011302003368号